ARCH 653: PROJECT 1-NEW MUSEUM OF CONTEMPORARY ART
The form of the building was derived from an additive process and can be described as a series of seven asymmetrical boxes stacked on one another according to the anticipated needs and circulation patterns of building users, different levels were driven away from the vertebrae of the building core laterally to the north, south, east, or west.
MASS MODELING:
ASSIGNING PARAMETRIC FEATURES:
PARAMETRIC BUILDING FACADE:
 |
| source:http://www.archdaily.com/70822/new-art-museum-sanaa/ |
Location: 235
Bowery, New York, NY 10002
Architectural Firms:
Gensler, SANAA
Architectural style:
Modern architecture (de-constructivism)
Height:
177.16 ft.
Total Floor Area:
58,700 ft2
Facade material:
aluminum
Facade system:
curtain wall
Main usage:
museum (fine arts)
DESIGN INTENT:
The form of the building was derived from an additive process and can be described as a series of seven asymmetrical boxes stacked on one another according to the anticipated needs and circulation patterns of building users, different levels were driven away from the vertebrae of the building core laterally to the north, south, east, or west.
The distinctive form of
the building was designed as a solution to fundamental challenges of an overcrowded site.
The shifted-box approach gives wider internal spaces that are different heights
at every level, with different characters and are column free.
MASS MODELING:
For modeling the
conceptual mass of the structure,horizontal reference planes were created at the start
and end of each box at a varied spacing equal to the height of each
box. Vertical reference planes were then positioned aligned to the face of each
box that is at an offset from the one below. This allows the blocks to stay in
place without moving dis-proportionally from each other when varied
parmetrically .The subsequent process is pretty straight forward, i.e to
sketch the foot prints of the boxes at each level and create an extrusion.
ASSIGNING PARAMETRIC FEATURES:
In relation to characteristic of the form, appropriate
way to parameterize, was to vary the size of each with respect to the size of
the box below it. Thus the length and width of each block is parametrically
related with the other and all the boxes vary in their size with the base
block.
The height of each block can also be varied
simultaneously, and is related to the floor height. Each block hosts two to
three stories and thus its height changes with the height of each floor.
Screenshots of the parametrically varied model are
presented below.
PARAMETRIC BUILDING FACADE:
The building facade modeled for the purpose of the project is a wave pattern that surrounds the
building mass.It is slightly different from the actual one.The
pictures here explain the procedure for creating the curtain panel.
In the curtain panel created, the parametric feature
to talk about would be the shape of the panel itself. By varying the value of
amplitude in the wave equation different shapes of panels can be achieved.
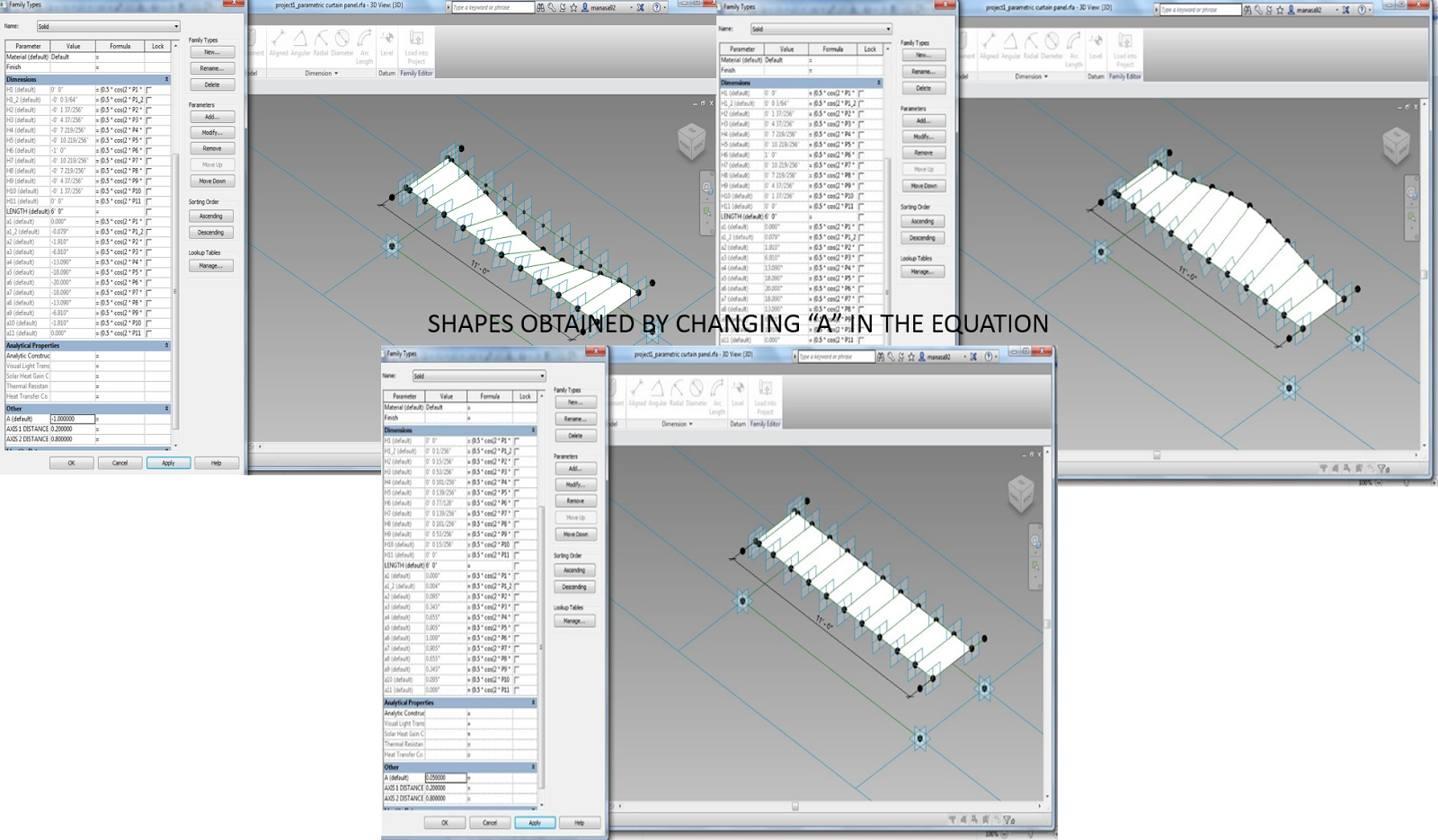 |
| Parametrically varied shapes of the panel |
 |
| Building mass with curtain panel RENDERINGS |
The curtain panel is an anodized aluminium mesh surrounding the vertical faces of the building hiding windows,balconies an balustrades . The facade appearance and material play a vital role for the building, the white color emphasizes the volume of the boxes which is important for a form like this.The white color gives a clean and light view to the structure in a massive cityscape like Manhattan.The front face of the the gallery is 15 ft high curtain wall , which attracts sight of the passers by towards the art pieces displayed in the lobby of the gallery.
REFERENCES
AUTO DESK SEEK
AUTODESK BIM CIRRICULUM
http://design.rootiers.it/tecniche2012/node/1255












.jpg)



